
We are pleased to share with you the 50 most read Nature Communications articles* in life and biological sciences published in 2019. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an international community.
Browse all Top 50 subject area collections here.
*Based on data from Google Analytics, covering January-December 2019 (data has been normalised to account for articles published later in the year)

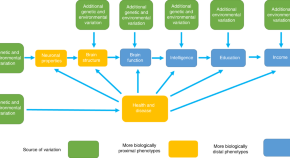
Household income is used as a marker of socioeconomic position, a trait that is associated with better physical and mental health. Here, Hill et al. report a genome-wide association study for household income in the UK and explore its relationship with intelligence in post-GWAS analyses including Mendelian randomization.
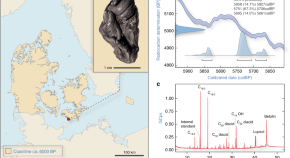
Birch pitch is thought to have been used in prehistoric times as hafting material or antiseptic and tooth imprints suggest that it was chewed. Here, the authors report a 5,700 year-old piece of chewed birch pitch from Denmark from which they successfully recovered a complete ancient human genome and oral microbiome DNA.
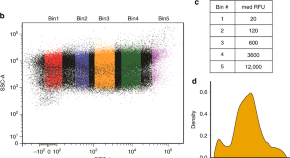
Several factors contribute to the efficiency of protein expression. Here the authors show that the identity of amino acids encoded by codons at position 3–5 significantly impact translation efficiency and protein expression levels.
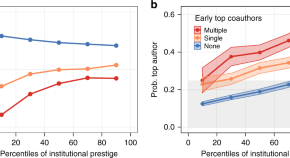
By examining publication records of scientists from four disciplines, the authors show that coauthoring a paper with a top-cited scientist early in one's career predicts lasting increases in career success, especially for researchers affiliated with less prestigious institutions.

Remains of several hundred humans are scattered around Roopkund Lake, situated over 5,000 meters above sea level in the Himalayan Mountains. Here the authors analyze genome-wide data from 38 skeletons and find 3 clusters with different ancestries and dates, showing the people were desposited in multiple catastrophic events.
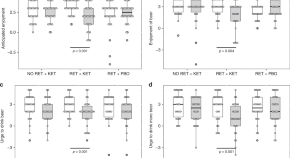
Memories linking environmental cues to alcohol reward are involved in the development and maintenance of heavy drinking. Here, the authors show that a single dose of ketamine, given after retrieval of alcohol-reward memories, disrupts the reconsolidation of these memories and reduces drinking in humans.
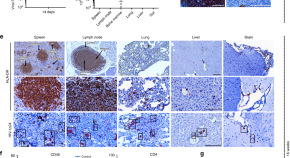
Here, the authors show that sequential treatment with long-acting slow-effective release ART and AAV9- based delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 results in undetectable levels of virus and integrated DNA in a subset of humanized HIV-1 infected mice. This proof-of-concept study suggests that HIV-1 elimination is possible.
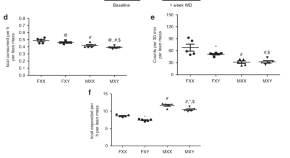
Men and women differ in their risk of developing coronary artery disease, in part due to differences in their levels of sex hormones. Here, AlSiraj et al. show that the XX sex genotype regulates lipid metabolism and promotes atherosclerosis independently of sex hormones in mice.
Little is known about the long-term effects of early-career setback. Here, the authors compare junior scientists who were awarded a NIH grant to those with similar track records, who were not, and find that individuals with the early setback systematically performed better in the longer term.
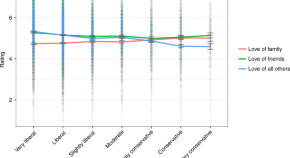
How do liberals and conservatives differ in their expression of compassion and moral concern? The authors show that conservatives tend to express concern toward smaller, more well-defined, and less permeable social circles, while liberals express concern toward larger, less well-defined, and more permeable social circles.
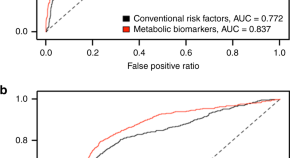
Biomarkers that predict mortality are of interest for clinical as well as research applications. Here, the authors analyze metabolomics data from 44,168 individuals and identify key metabolites independently associated with all-cause mortality risk.

Numerous feathered dinosaurs and early birds have been discovered from the Jurassic and Cretaceous, but the early evolution of feather-feeding insects is not clear. Here, Gao et al. describe a new family of ectoparasitic insects from 10 specimens found associated with feathers in mid-Cretaceous amber.
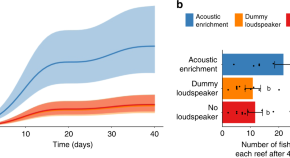
Healthy coral reefs have an acoustic signature known to be attractive to coral and fish larvae during settlement. Here the authors use playback experiments in the field to show that healthy reef sounds can increase recruitment of juvenile fishes to degraded coral reef habitat, suggesting that acoustic playback could be used as a reef management strategy.
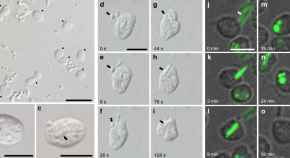
Phagocytosis is a typically eukaryotic feature that could be behind the origin of eukaryotic cells. Here, the authors describe a bacterium that can engulf other bacteria and small eukaryotic cells through a phagocytosis-like mechanism.
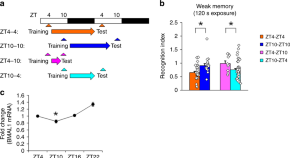
The neural mechanisms that lead to a relative deficit in memory retrieval in the afternoon are unclear. Here, the authors show that the circadian - dependent transcription factor BMAL1 regulates retrieval through dopamine and glutamate receptor phosphorylation.
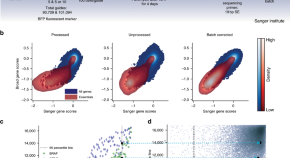
Integrating independent large-scale pharmacogenomic screens can enable unprecedented characterization of genetic vulnerabilities in cancers. Here, the authors show that the two largest independent CRISPR-Cas9 gene-dependency screens are concordant, paving the way for joint analysis of the data sets.
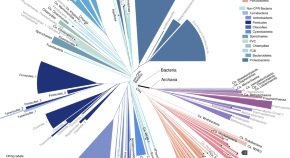
The authors build a reference phylogeny of 10,575 evenly-sampled bacterial and archaeal genomes, based on 381 markers. The results indicate a remarkably closer evolutionary proximity between Archaea and Bacteria than previous estimates that used fewer “core” genes, such as the ribosomal proteins.
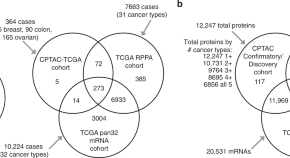
Mass-spectrometry-based profiling can be used to stratify tumours into molecular subtypes. Here, by classifying over 500 tumours, the authors show that this approach reveals proteomic subgroups which cut across tumour types.
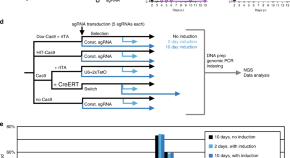
Inducible genome editing systems often suffer from leakiness or reduced activity. Here the authors develop CRISPR-Switch, a Cre recombinase ON/OFF-controlled sgRNA cassette that allows consecutive editing of two loci.
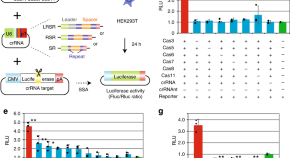
Class 1 CRISPR systems are not as developed for genome editing as Class 2 systems are. Here the authors show that Cas3 can be used to generate functional knockouts and knock-ins, as well as Cas3-mediated exon-skipping in DMD cells.
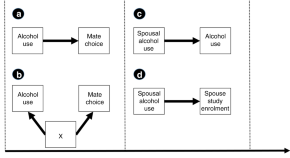
From observational studies, alcohol consumption behaviours are known to be correlated in spouses. Here, Howe et al. use partners’ genotypic information in a Mendelian randomization framework and show that a SNP in the ADH1B gene associates with partner’s alcohol consumption, suggesting that alcohol consumption affects mate choice.
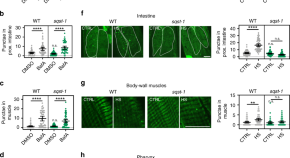
While the cellular recycling process autophagy has been linked to aging, the impact of selective autophagy on lifespan remains unclear. Here Kumsta et al. show that the autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1 is required for hormetic benefits and p62/SQSTM1 overexpression is sufficient to extend C. elegans lifespan and improve proteostasis.

Recent studies have suggested that hybridization can facilitate adaptive radiations. Here, the authors show that opportunity for hybridization differentiates Lake Mweru, where cichlids radiated, and Lake Bangweulu, where cichlids did not radiate despite ecological opportunity in both lakes.
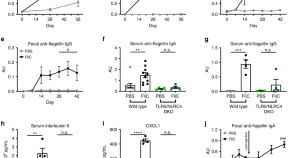
Gut microbiota alterations, including enrichment of flagellated bacteria, are associated with metabolic syndrome and chronic inflammatory diseases. Here, Tran et al. show, in mice, that elicitation of mucosal anti-flagellin antibodies protects against experimental colitis and ameliorates diet-induced obesity.
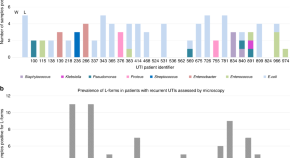
The reservoir for recurrent urinary tract infection in humans is unclear. Here, Mickiewicz et al. detect cell-wall deficient (L-form) E. coli in fresh urine from patients, and show that the isolated bacteria readily switch between walled and L-form states.
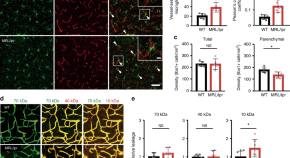
Although it is known that microglia respond to injury and systemic disease in the brain, it is unclear if they modulate blood–brain barrier (BBB) integrity, which is critical for regulating neuroinflammatory responses. Here authors demonstrate that microglia respond to inflammation by migrating towards and accumulating around cerebral vessels, where they initially maintain BBB integrity via expression of the tight-junction protein Claudin-5 before switching, during sustained inflammation, to phagocytically remove astrocytic end-feet resulting in impaired BBB function
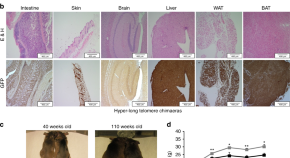
Telomere shortening is associated with aging. Here the authors analyze mice with hyperlong telomeres and demonstrate that longer telomeres than normal have beneficial effects such as delayed metabolic aging, increased longevity and less incidence of cancer.
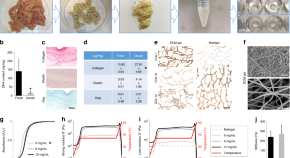
Organoid cultures have been developed from multiple tissues, opening new possibilities for regenerative medicine. Here the authors demonstrate the derivation of GMP-compliant hydrogels from decellularized porcine small intestine which support formation and growth of human gastric, liver, pancreatic and small intestinal organoids.
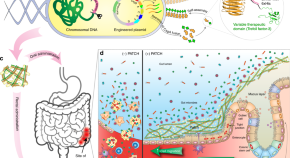
Anti-inflammatory treatments for gastrointestinal diseases can often have detrimental side effects. Here the authors engineer E. coli Nissle 1917 to create a fibrous matrix that has a protective effect in DSS-induced colitis mice.
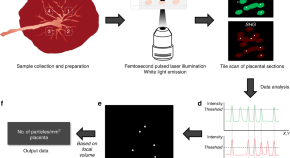
Exposure to air pollution during pregnancy has been associated with impaired birth outcomes. Here, Bové et al. report evidence of black carbon particle deposition on the fetal side of human placentae, including at early stages of pregnancy, suggesting air pollution could affect birth outcome through direct effects on the fetus.
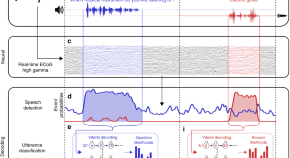
Speech neuroprosthetic devices should be capable of restoring a patient’s ability to participate in interactive dialogue. Here, the authors demonstrate that the context of a verbal exchange can be used to enhance neural decoder performance in real time.
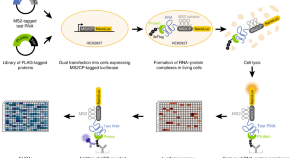
RNA-interacting proteome can be identified by RNA affinity purification followed by mass spectrometry. Here the authors developed a different RNA-centric technology that combines high-throughput immunoprecipitation of RNA binding proteins and luciferase-based detection of their interaction with the RNA.
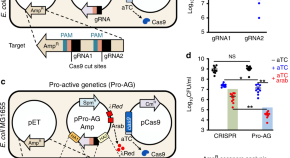
Genedrives bias the inheritance of alleles in diploid organisms. Here, the authors develop a gene-drive analogous system for bacteria, selectively editing and clearing plasmids.
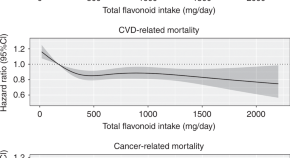
The studies showing health benefits of flavonoids and their impact on cancer mortality are incomplete. Here, the authors perform a prospective cohort study in Danish participants and demonstrate an inverse association between regular flavonoid intake and both cardiovascular and cancer related mortality.
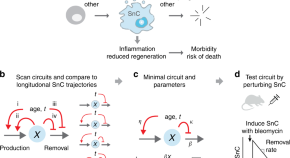
One of the underlying causes of aging is the accumulation of senescent cells, but their turnover rates and dynamics during ageing are unknown. Here the authors measure and model senescent cell production and removal and explore implications for mortality.
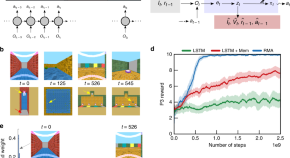
People are able to mentally time travel to distant memories and reflect on the consequences of those past events. Here, the authors show how a mechanism that connects learning from delayed rewards with memory retrieval can enable AI agents to discover links between past events to help decide better courses of action in the future.
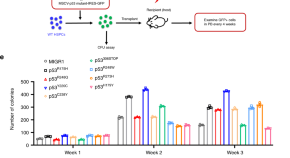
Ageing is associated with clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), which is linked to increased risks of hematological malignancies. Here the authors uncover an epigenetic mechanism through which mutant p53 drives clonal hematopoiesis through interaction with EZH2.
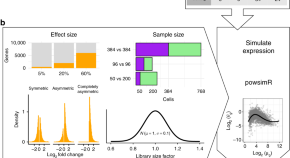
There has been a rapid rise in single cell RNA-seq methods and associated pipelines. Here the authors use simulated data to systematically evaluate the performance of 3000 possible pipelines to derive recommendations for data processing and analysis of different types of scRNA-seq experiments.
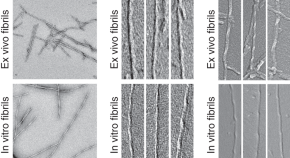
Alzheimer’s disease is characterised by the deposition of Aβ amyloid fibrils and tau protein neurofibrillary tangles. Here the authors use cryo-EM to structurally characterise brain derived Aβ amyloid fibrils and find that they are polymorphic and right-hand twisted, which differs from in vitro generated Aβ fibrils.
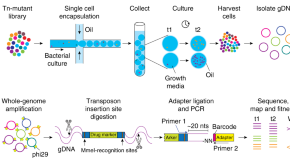
Culturing transposon-mutant libraries in pools can mask complex phenotypes. Here the authors present microfluidics mediated droplet Tn-Seq, which encapsulates individual mutants, promotes isolated growth and enables cell-cell interaction analyses.
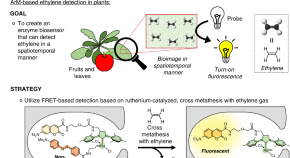
Existing methods to detect ethylene in plant tissue typically require gas chromatography or use ethylene-dependent gene expression as a proxy. Here Vong et al. show that an artificial metalloenzyme-based ethylene probe can be used to detect ethylene in plants with improved spatiotemporal resolution.
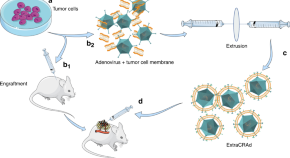
Cancer therapy using oncolytic virus has shown pre-clinical and clinical efficacy. Here, the authors report ExtraCRAd, an oncolytic virus cloaked with tumour cell membrane and report its therapeutic effects in vitro and in vivo in multiple mouse tumour models.
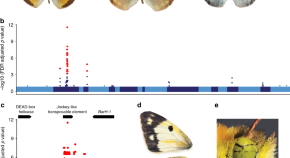
Tradeoffs are central to life history theory and evolutionary biology, yet almost nothing is known about their mechanistic basis. Here the authors characterize one such mechanism and find a transposable element insertion is associated with the switch between alternative life history strategies.
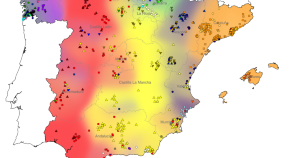
The Iberian Peninsula has a complex history. Here, the authors analyse the genetic structure of the modern Iberian population at fine scale, revealing historical population movements associated with the time of Muslim rule.
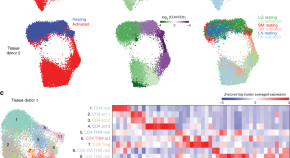
Immune cells are shaped by the tissue environment, yet the states of healthy human T cells are mainly studied in the blood. Here, the authors perform single cell RNA-seq of T cells from tissues and blood of healthy donors and show its utility as a reference map for comparison of human T cell states in disease.
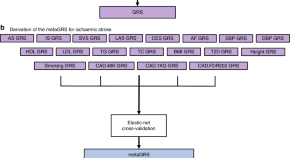
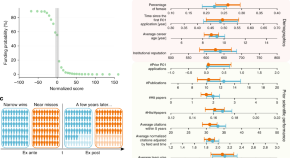
Stroke risk is influenced by genetic and lifestyle factors and previously a genomic risk score (GRS) for stroke was proposed, albeit with limited predictive power. Here, Abraham et al. develop a metaGRS that is composed of several stroke-related GRSs and demonstrate improved predictive power compared with individual GRS or classic risk factors.
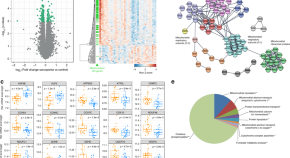
Sarcopenia is the loss of muscle mass and strength associated with physical disability during ageing. Here, the authors analyse muscle biopsies from 119 patients with sarcopenia and age-matched controls of different ethnic groups and find transcriptional signatures indicating mitochondrial dysfunction, associated with reduced mitochondria numbers and lower NAD + levels in older individuals with sarcopenia.
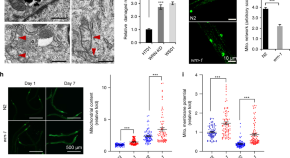
The molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction in the premature ageing Werner syndrome were elusive. Here the authors show that NAD + depletion-induced impaired mitophagy contributes to this phenomenon, shedding light on potential therapeutics.
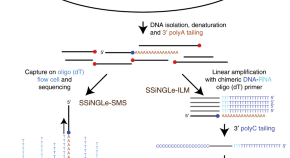
Single strand breaks represent the most common form of DNA damage yet no methods to map them in a genome-wide fashion at single nucleotide resolution exist. Here the authors develop such a method and apply to uncover patterns of single-strand DNA “breakome” in different biological conditions.
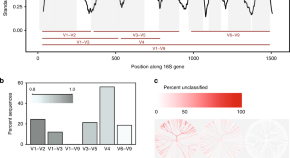
Here, the authors explore the potential of the 16S gene for discriminating bacterial taxa and show that full-length sequencing combined with appropriate clustering of intragenomic sequence variation can provide accurate representation of bacterial species in microbiome datasets.